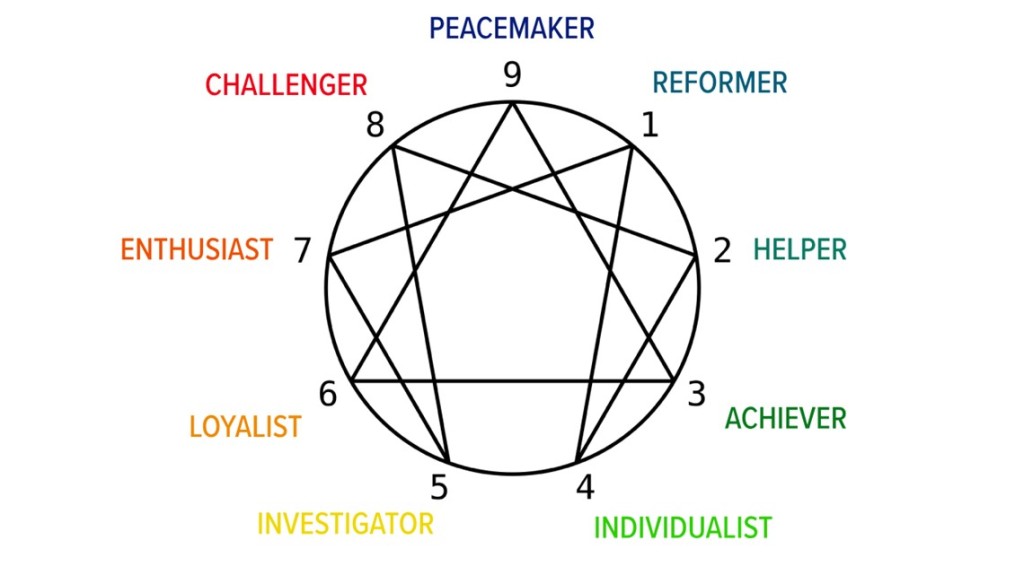
9 Archetypes
The Personality Enneagram consists of 9 different archetypes, going from 1-9 (see image above). We call this our “main type“, or our “primary type“. But once you know your main type, you can figure out what wing you have.
Every person has one wing, or secondary type, that sits to the side of one’s primary type (see image below). This creates:
- 9 main types
- 18 subtypes
Basic Fear & Desire
Each type come with a basic:
- Fear
- Desire (and)
- Vice
Here is a chart:
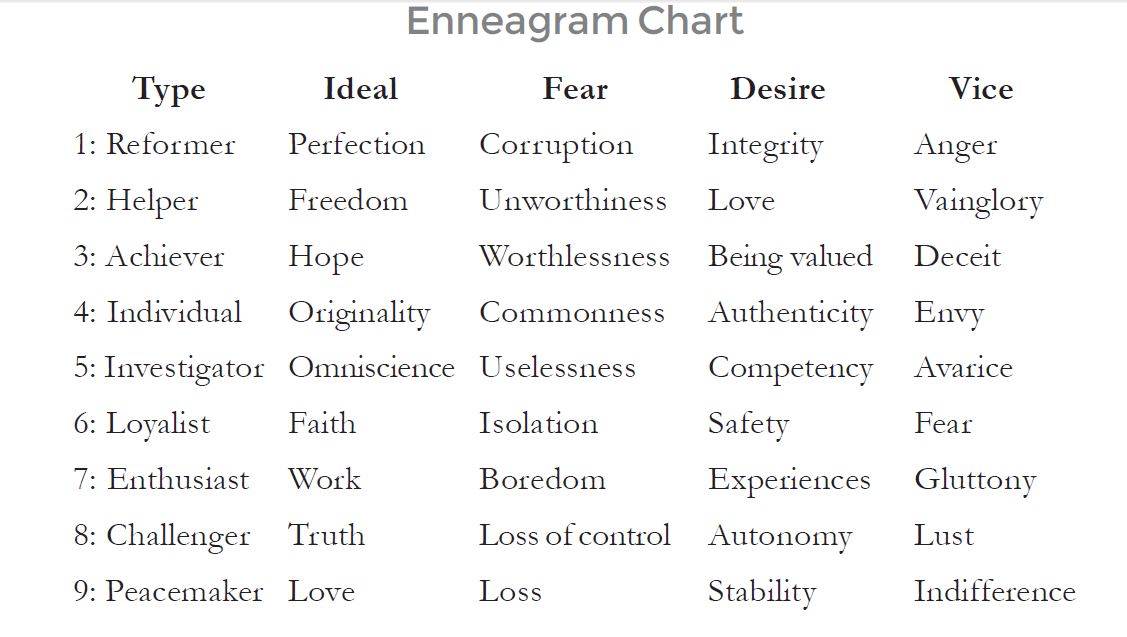
Which one are you??!!
The 9 Types
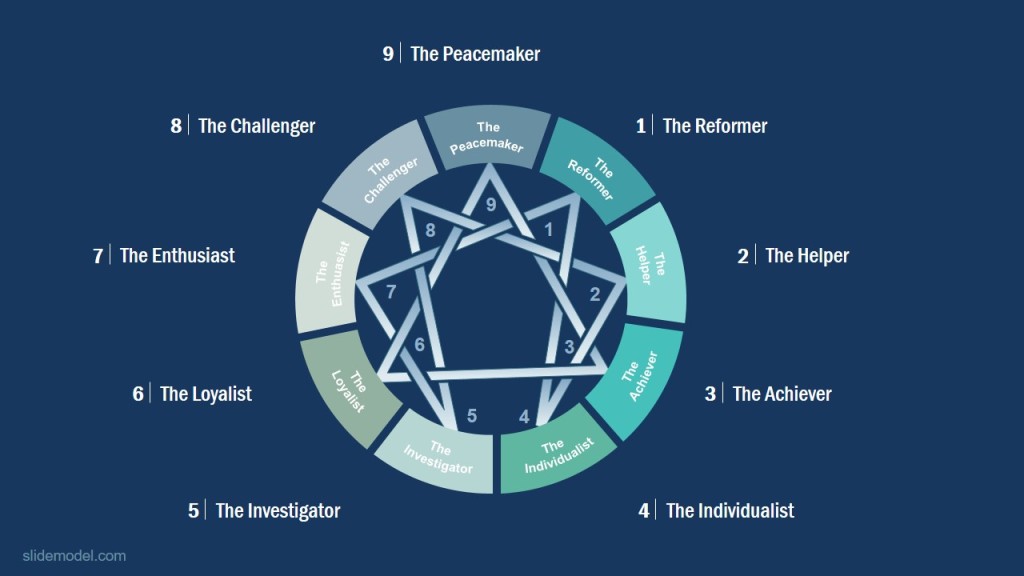
- Type 1: The Perfectionist
- Type 2: The Helper
- Type 3: The Achiever
- Type 4: The Individualist
- Type 5: The Investigator
- Type 6: The Loyalist
- Type 7: The Enthusiast
- Type 8: The Challenger
- Type 9: The Peacemaker
Type 1: The Perfectionist

Ones are conscientious and ethical, with a strong sense of right and wrong. They are teachers, crusaders, and advocates for change: always striving to improve things, but afraid of making a mistake. Well-organized, orderly, and fastidious, they try to maintain high standards, but can slip into being critical and perfectionistic. They typically have problems with resentment and impatience. At their Best: wise, discerning, realistic, and noble. Can be morally heroic.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Basic Fear: Of being corrupt/evil, defective.
- Basic Desire: To be good, to have integrity, to be balanced.
Key Motivations: Want to be right, to strive higher and improve everything, to be consistent with their ideals, to justify themselves, to be beyond criticism — so as not to be condemned by anyone.
Ones often persuade themselves that they are “head” types, rationalists who proceed only on logic and objective truth. But, the real picture is somewhat different: Ones are actually activists who are searching for an acceptable rationale for what they feel they must do. They are people of instinct and passion who use convictions and judgments to control and direct themselves and their actions.
In the effort to stay true to their principles, Ones resist being affected by their instinctual drives, consciously not giving in to them or expressing them too freely. The result is a personality type that has problems with repression, resistance, and aggression. They are usually seen by others as highly self- controlled, even rigid, although this is not how Ones experience themselves. It seems to them that they are sitting on a cauldron of passions and desires, and they had better “keep the lid on” lest they and everyone else around them regret it.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Type 2: The Helper

THE HELPER: The Caring, Interpersonal Type:
Generous, Demonstrative, People-Pleasing, and Possessive.
Twos are empathetic, sincere, and warm-hearted. They are friendly, generous, and self-sacrificing, but can also be sentimental, flattering, and people-pleasing. They are well-meaning and driven to be close to others, but can slip into doing things for others in order to be needed. They typically have problems with possessiveness and with acknowledging their own needs. At their Best: unselfish and altruistic, they have unconditional love for others.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Basic Fear: Of being unwanted, unworthy of being loved.
- Basic Desire: To feel loved.
Key Motivations: Want to be loved, to express their feelings for others, to be needed and appreciated, to get others to respond to them, to vindicate their claims about themselves.
Being generous and going out of their way for others makes Twos feel that theirs is the richest, most meaningful way to live. The love and concern they feel—and the genuine good they do—warms their hearts and makes them feel worthwhile. Twos are most interested in what they feel to be the “really, really good” things in life—love, closeness, sharing, family, and friendship.
However, Twos’ inner development may be limited by their “shadow side”—pride, self-deception, the tendency to become over-involved in the lives of others, and the tendency to manipulate others to get their own emotional needs met. Transformational work entails going into dark places in ourselves, and this very much goes against the grain of the Two’s personality structure, which prefers to see itself in only the most positive, glowing terms.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Type 3: The Achiever

Threes are self-assured, attractive, and charming. Ambitious, competent, and energetic, they can also be status-conscious and highly driven for advancement. They are diplomatic and poised, but can also be overly concerned with their image and what others think of them. They typically have problems with workaholism and competitiveness. At their Best: self-accepting, authentic, everything they seem to be—role models who inspire others.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Fear: Of being worthless.
- Basic Desire: To feel valuable and worthwhile.
Key Motivations: Want to be affirmed, to distinguish themselves from others, to have attention, to be admired, and to impress others.
Everyone needs attention, encouragement, and the affirmation of their value in order to thrive, and Threes are the type which most exemplifies this universal human need. Threes want success not so much for the things that success will buy (like Sevens), or for the power and feeling of independence that it will bring (like Eights). They want success because they are afraid of disappearing into a chasm of emptiness and worthlessness: without the increased attention and feeling of accomplishment which success usually brings, Threes fear that they are nobody and have no value.
The problem is that, in the headlong rush to achieve whatever they believe will make them more valuable, Threes can become so alienated from themselves that they no longer know what they truly want, or what their real feelings or interests are. In this state, they are easy prey to self–deception, deceit, and falseness of all kinds. Thus, the deeper problem is that their search for a way to be of value increasingly takes them further away from their own Essential Self with its core of real value.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Examples of Type 3s:
- Adolf Hitler was an INTJ 3wing4
- Tom Cruise is an ESTP 3wing4
- Dana White is an ESTJ 3wing2
- Barack Obama is an INTP 3wing2
Type 4: The Individualist

Fours are self-aware, sensitive, and reserved. They are emotionally honest, creative, and personal, but can also be moody and self-conscious. Withholding themselves from others due to feeling vulnerable and defective, they can also feel disdainful and exempt from ordinary ways of living. They typically have problems with melancholy, self-indulgence, and self-pity. At their Best: inspired and highly creative, they are able to renew themselves and transform their experiences.
- Basic Fear: That they have no identity or personal significance.
- Basic Desire: To find themselves and their significance (to create an identity).
Key Motivations: Want to express themselves and their individuality, to create and surround themselves with beauty, to maintain certain moods and feelings, to withdraw to protect their self-image, to take care of emotional needs before attending to anything else, to attract a “rescuer.”
While it is true that Fours often feel different from others, they do not really want to be alone. They may feel socially awkward or self-conscious, but they deeply wish to connect with people who understand them and their feelings. The “romantics” of the Enneagram, they long for someone to come into their lives and appreciate the secret self that they have privately nurtured and hidden from the world.
If, over time, such validation remains out of reach, Fours begin to build their identity around how unlike everyone else they are. The outsider therefore comforts herself by becoming an insistent individualist: everything must be done on her own, in her own way, on her own terms. Fours’ mantra becomes “I am myself. Nobody understands me. I am different and special,” while they secretly wish they could enjoy the easiness and confidence that others seem to enjoy.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Examples of Type 4s:
- Johnny Depp is an INFJ 4wing5
- Kanye West is an ISFP 4wing5
- Michael Jackson was an ISFP 4wing3
- Jon Jones is an INTP 4wing3
Type 5: The Investigator

THE INVESTIGATOR: The Intense, Cerebral Type:
Perceptive, Innovative, Secretive, and Isolated.
Fives are alert, insightful, and curious. They are able to concentrate and focus on developing complex ideas and skills. Independent, innovative, and inventive, they can also become preoccupied with their thoughts and imaginary constructs. They become detached, yet high-strung and intense. They typically have problems with eccentricity, nihilism, and isolation. At their Best: visionary pioneers, often ahead of their time, and able to see the world in an entirely new way.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Basic Fear: Being useless, helpless, or incapable.
- Basic Desire: To be capable and competent.
Key Motivations: Want to possess knowledge, to understand the environment, to have everything figured out as a way of defending the self from threats from the environment.
We have named personality type Five The Investigator because, more than any other type, Fives want to find out why things are the way they are. They want to understand how the world works, whether it is the cosmos, the microscopic world, the animal, vegetable, or mineral kingdoms—or the inner world of their imaginations. They are always searching, asking questions, and delving into things in depth. They do not accept received opinions and doctrines, feeling a strong need to test the truth of most assumptions for themselves.
Knowledge, understanding, and insight are thus highly valued by Fives, because their identity is built around “having ideas” and being someone who has something unusual and insightful to say. For this reason, Fives are not interested in exploring what is already familiar and well-established; rather, their attention is drawn to the unusual, the overlooked, the secret, the occult, the bizarre, the fantastic, the “unthinkable.”
Investigating “unknown territory”—knowing something that others do not know, or creating something that no one has ever experienced—allows Fives to have a niche for themselves that no one else occupies. They believe that developing this niche is the best way that they can attain independence and confidence.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Example of a Type 5:
- Elon Musk is an INTP 5wing4 (my most popular page)
Type 6: The Loyalist

THE LOYALIST: The Committed, Security-Oriented Type:
Engaging, Responsible, Anxious, and Suspicious.
The committed, security-oriented type. Sixes are reliable, hard-working, responsible, and trustworthy. Excellent “troubleshooters,” they foresee problems and foster cooperation, but can also become defensive, evasive, and anxious—running on stress while complaining about it. They can be cautious and indecisive, but also reactive, defiant and rebellious. They typically have problems with self-doubt and suspicion. At their Best: internally stable and self-reliant, courageously championing themselves and others.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Basic Fear: Of being without support and guidance.
- Basic Desire: To have security and support.
Key Motivations: Want to have security, to feel supported by others, to have certitude and reassurance, to test the attitudes of others toward them, to fight against anxiety and insecurity.
The reason Sixes are so loyal to others is that they do not want to be abandoned and left without support—their Basic Fear. Thus, the central issue for type Six is a failure of self-confidence. Sixes come to believe that they do not possess the internal resources to handle life’s challenges and vagaries alone, and so increasingly rely on structures, allies, beliefs, and supports outside themselves for guidance to survive. If suitable structures do not exist, they will help create and maintain them.
The biggest problem for Sixes is that they try to build safety in the environment without resolving their own emotional insecurities. When they learn to face their anxieties, however, Sixes understand that although the world is always changing and is, by nature uncertain, they can be serene and courageous in any circumstance. And they can attain the greatest gift of all, a sense of peace with themselves despite the uncertainties of life.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Type 7: The Enthusiast

THE ENTHUSIAST: The Busy, Variety-Seeking Type:
Spontaneous, Versatile, Acquisitive, and Scattered.
Sevens are extroverted, optimistic, versatile, and spontaneous. Playful, high-spirited, and practical, they can also misapply their many talents, becoming over-extended, scattered, and undisciplined. They constantly seek new and exciting experiences, but can become distracted and exhausted by staying on the go. They typically have problems with impatience and impulsiveness. At their Best: they focus their talents on worthwhile goals, becoming appreciative, joyous, and satisfied.
- Basic Fear: Of being deprived and in pain.
- Basic Desire: To be satisfied and content—to have their needs fulfilled.
Key Motivations: Want to maintain their freedom and happiness, to avoid missing out on worthwhile experiences, to keep themselves excited and occupied, to avoid and discharge pain.
Sevens are frequently endowed with quick, agile minds, and can be exceptionally fast learners. This is true both of their ability to absorb information (language, facts, and procedures) and their ability to learn new manual skills—they tend to have excellent mind-body coordination, and manual dexterity (typewriting, piano playing, tennis). All of this can combine to make a Seven into the quintessential “Renaissance person.”
Sevens cope with anxiety in two ways. First, they try to keep their minds busy all of the time. As long as Sevens can keep their minds occupied, especially with projects and positive ideas for the future, they can, to some extent, keep anxiety and negative feelings out of conscious awareness. Likewise, since their thinking is stimulated by activity, Sevens are compelled to stay on the go, moving from one experience to the next, searching for more stimulation. This is not to say that Sevens are “spinning their wheels.” They generally enjoy being practical and getting things done.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Examples of Type 7s:
Type 8: The Challenger

Eights are self-confident, strong, and assertive. Protective, resourceful, straight-talking, and decisive, but can also be ego-centric and domineering. Eights feel they must control their environment, especially people, sometimes becoming confrontational and intimidating. Eights typically have problems with their tempers and with allowing themselves to be vulnerable. At their Best: self- mastering, they use their strength to improve others’ lives, becoming heroic, magnanimous, and inspiring.
— The Enneagram Institute
- Basic Fear: Of being harmed or controlled by others.
- Basic Desire: To protect themselves (to be in control of their own life and destiny).
Key Motivations: Want to be self-reliant, to prove their strength and resist weakness, to be important in their world, to dominate the environment, and to stay in control of their situation.
Eights have enormous willpower and vitality, and they feel most alive when they are exercising these capacities in the world. They use their abundant energy to effect changes in their environment—to “leave their mark” on it—but also to keep the environment, and especially other people, from hurting them and those they care about. At an early age, Eights understand that this requires strength, will, persistence, and endurance—qualities that they develop in themselves and which they look for in others.
Eights do not want to be controlled or to allow others to have power over them (their Basic Fear), whether the power is psychological, sexual, social, or financial. Much of their behavior is involved with making sure that they retain and increase whatever power they have for as long as possible. An Eight may be a general or a gardener, a small businessman or a mogul, the mother of a family or the superior of a religious community. No matter: being “in charge” and leaving their imprint on their sphere is uniquely characteristic of them.
Eights are the true “rugged individualists” of the Enneagram. More than any other type, they stand alone. They want to be independent, and resist being indebted to anyone. They often refuse to “give in” to social convention, and they can defy fear, shame, and concern about the consequences of their actions. Although they are usually aware of what people think of them, they do not let the opinions of others sway them. They go about their business with a steely determination that can be awe inspiring, even intimidating to others.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Examples of Type 8s:
- Conor McGregor is an ISTP 8wing7
- Alex Jones is an INTJ 8wing7
- Eddie Bravo is an INTP 8wing7
- Howard Stern is an INTJ 8wing9
Type 9: The Peacemaker

THE PEACEMAKER: The Easygoing, Self-Effacing Type:
Receptive, Reassuring Agreeable, and Complacent.
Nines are accepting, trusting, and stable. They are usually creative, optimistic, and supportive, but can also be too willing to go along with others to keep the peace. They want everything to go smoothly and be without conflict, but they can also tend to be complacent, simplifying problems and minimizing anything upsetting. They typically have problems with inertia and stubbornness. At their Best: indomitable and all-embracing, they are able to bring people together and heal conflicts.
- Basic Fear: Of loss and separation.
- Basic Desire: To have inner stability “peace of mind”.
Key Motivations: Want to create harmony in their environment, to avoid conflicts and tension, to preserve things as they are, to resist whatever would upset or disturb them.
We have called personality type Nine The Peacemaker because no type is more devoted to the quest for internal and external peace for themselves and others. They are typically “spiritual seekers” who have a great yearning for connection with the cosmos, as well as with other people.
They work to maintain their peace of mind just as they work to establish peace and harmony in their world. The issues encountered in the Nine are fundamental to all psychological and spiritual work—being awake versus falling asleep to our true nature; presence versus entrancement, openness versus blockage, tension versus relaxation, peace versus pain, union versus separation.
We have sometimes called the Nine the crown of the Enneagram because it is at the top of the symbol and because it seems to include the whole of it. Nines can have the strength of Eights, the sense of fun and adventure of Sevens, the dutifulness of Sixes, the intellectualism of Fives, the creativity of Fours, the attractiveness of Threes, the generosity of Twos, and the idealism of Ones. However, what they generally do not have is a sense of really inhabiting themselves—a strong sense of their own identity.
Nines demonstrate the universal temptation to ignore the disturbing aspects of life and to seek some degree of peace and comfort by “numbing out.” They respond to pain and suffering by attempting to live in a state of premature peacefulness, whether it is in a state of false spiritual attainment, or in more gross denial. More than any other type, Nines demonstrate the tendency to run away from the paradoxes and tensions of life by attempting to transcend them or by seeking to find simple and painless solutions to their problems.
Jump to the top of the chapter.
Examples of Type 9s: